Which of the Following Is Diagnostic for Neisseria Meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis often referred to as meningococcus is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia a life-threatening sepsisThe bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. Pneumoniae - by 67.
Neisseria Meningitidis Gonorrhea Std Information From Cdc
Meningitidis - by 356.

. About 10 of adults are. Program monitoring and management. Digital health technologies have different functions and can be used as solutions in the following areasPatient care.
Children and infants may show different signs and symptoms such as inactivity irritability vomiting or poor reflexes. The procedures described in this manual are not new. Neisseria meningitidis specimen nucleic acids are tested using a Real-Time polymerase chain reaction PCR detection of a Neisseria meningitidis carbohydrate transporter ctrA and capsular biosynthesis genes for serogroups A B C W135 X and Y.
Among 115 cases of N. Microbial Sensitivity Tests Neisseria meningitidis isolation purification Penicillin G Procaine therapeutic use Penicillin Resistance Pneumonia diagnostic imaging Pneumonia drug therapy Pneumonia etiology Radiography Tetracycline therapeutic use Substances Penicillin G Procaine Tetracycline. One such test is the Pastorexrapid agglutination test Bio-Rad Laboratores Inc Marne-la-Coquette France which can detect Neisseria meningitidisN.
CSF culture is the gold standard for the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. The sensitivity of the Real Time PCR test is higher than conventional culture. Symptoms of septicemia include tiredness vomiting chills severe aches and pain fast breathing diarrhea and a dark rash.
E-learning for patients and health care workers. Influenzae b - by 192 it is possible to set them in the field and at the epidpoint if necessary. When compared to our laboratorys standard methodology results showed high concordance.
From the sinuses to the meninges bacteria can spread. Following bacteriologic diagnosis the patient was treated and responded to a course of penicillin therapy. This manual summarizes laboratory techniques used in the isolation and identification and characterization of Neisseria meningitidis the meningococcus Streptococcus pneumoniae the pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae from the cerebrospinal fluid or blood of patients with clinical meningitis or bacteremia.
Meningitidis infection in Japan during the last 9 years 22 191 were caused by serogroup B and 18 157 were caused by serogroup Y. In this review we describe the biology microbiology and epidemiology of this exclusive human pathogen. The recent advances in cellular microbiology genomics and immunology has opened new horizons in the understanding of meningococcal pathogenesis and in the definition of new prophylactic intervention.
Meningitidis can be developed as a result of pneumonia. Influenzae can be made on the basis of a cytological examination of the CSF specific colony morphology on blood andor chocolate agar staining properties on a Gram stain or by detection of specific antigens in the CSF by a latex agglutination test or using a rapid diagnostic test RDT. Up to 24 cash back The lungs air seems to be black.
Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus agalactiae group B strep Streptococcus pyogenes group A strep Neisseria meningitidis is immediately reportable on first knowledge or suspicion of the diagnosis due to. Production and immunochemical characterization of Neisseria meningitidis group B antiserum for the diagnosis of purulent meningitis Abstract Unlike Neisseria meningitidis groups A C Y and W135 the group B capsular polysaccharide has been shown to be chemically and immunologically identical to the capsular polysaccharide of Escherichia coli K1. Meningitidis serogroups A C and YW135 as well as N.
Laboratory methods for the diagnosis of meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae and. During the 1990s the serogroup C ST11ET37 complex was prominent in Europe. Neisseria-Kwik RIM-N Gonobio-Test Minitek Gonochek II GonoGen Phadebact Monoclonal GC OMNI Test and Syva MicroTrak Test.
Which of the following is diagnostic for Neisseria meningitidis. It is now clear that Neissera meningitidis has evolved a number of surface structures to mediate interaction with host cells and a. Dillon JR Carballo M Pauzé M.
Latex-agglutination test and immunochromatographic test allow to increase the identification of pathogens of BM for N. Fat and muscle show as grayscale images. A head CT scan may reveal issues such as a brain abscess or sinusitis.
If the carbohydrate utilization test indicates that the isolate may be N. Bacteria that cause meningococcal disease can also infect the blood causing septicemia. In children and teens meningococcus is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis.
The sensitivities for detection of Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae from CSF dried and stored on FTA TM cards were 98 92 and 100 respectively and with serum samples were 73 88 and 100 respectively. Meningitidis can be identified using Kovacs oxidase test and carbohydrate utilization. A the presence of Gram-negative diplococci in phagocytes of the central nervous system B its inability to ferment maltose C the presence of lipid A D the lack of lipooligosaccharide E the lack of fimbriae.
Meningitidisserogroup BEcoli Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniaeand Group B Streptococcus. Evaluation of eight methods for identification of pathogenic Neisseria species. Meningitidis serological tests to identify the serogroup should be performed.
Only 3 26 cases were caused by serotype W. 13 Diagnosing meningococci can also include analyzing peripheral blood skin lesions synovial fluid pleural fluid or pericardial fluid in patients suspected of having pneumonia septic arthritis or pericarditis due to N. Neisseria meningitidis the meningococcus causes significant morbidity and mortality in children and young adults worldwide through epidemic or sporadic meningitis andor septicemia.
The bacterium Neisseria meningitidis also called meningococcus causes meningococcal meningitis. 1010160732-8893 8890006-5 Abstract The clinical course of a malnourished alcoholic in which Neisseria meningitidis was isolated from the blood and Moraxella osloensis from the peritoneal fluid is described. If the oxidase test is positive carbohydrate utilization testing should be performed.
Pneumonia tuberculosis and fungal infection can all be detected using chest X-rays. Meningitidis ST11ET37 complex is a hyperinvasive lineage. Meningitidis is a fastidious encapsulated aerobic.
Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes group A strep Neisseria meningitidis is immediately reportable on first knowledge or suspicion of the diagnosis due to the potential need for prophylaxis of close contacts within 24 hours of suspected diagnosis suspicion is.
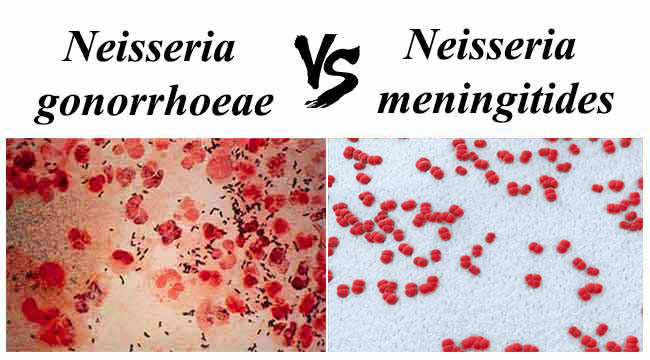
Difference Between Neisseria Gonorrhoeae And Neisseria Meningitidis Microbiology Info Com

Neisseria Meningitidis Gonorrhea Std Information From Cdc

Meningococcus Introduction Culture Characteristics Pathogenesis
No comments for "Which of the Following Is Diagnostic for Neisseria Meningitidis"
Post a Comment